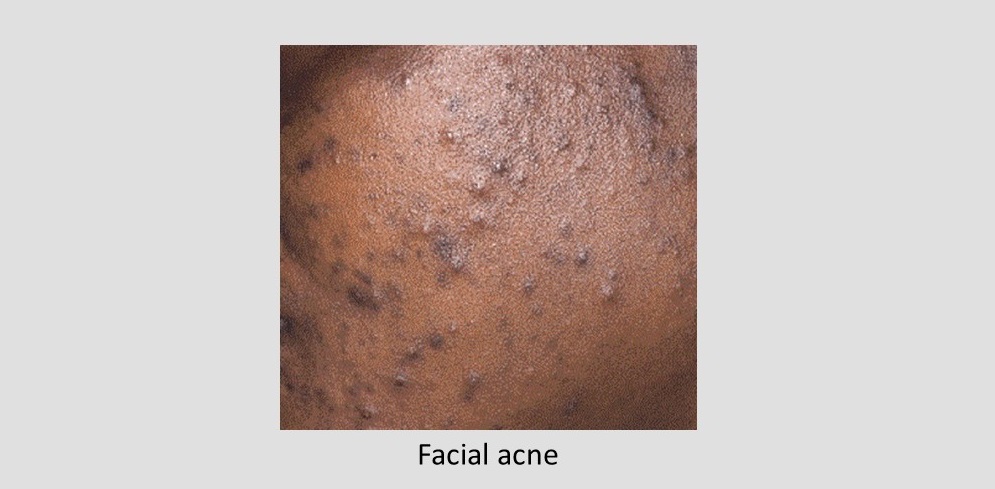
Do you want to get rid of acne fast?
Well, this article will cover everything that you need to know about acne; its causes, types, symptoms, prevention, and treatment.
What is acne?
Acne is the most common skin disorder diagnosed by dermatologists and other healthcare providers worldwide, and mostly affects young people. Children and adults are increasingly being affected too. The worldwide prevalence is ~9.4%. In adolescents, the prevalence is 65 - 75%. In Durban, South Africa (SA), acne is the second most common skin disease, with females mainly affected (1.75:1). Scarring and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) are the main consequences of acne. PIH is most common in African blacks and many patients are known to seek therapy for PIH even after the active lesions of acne have resolved.1
Common types of acne
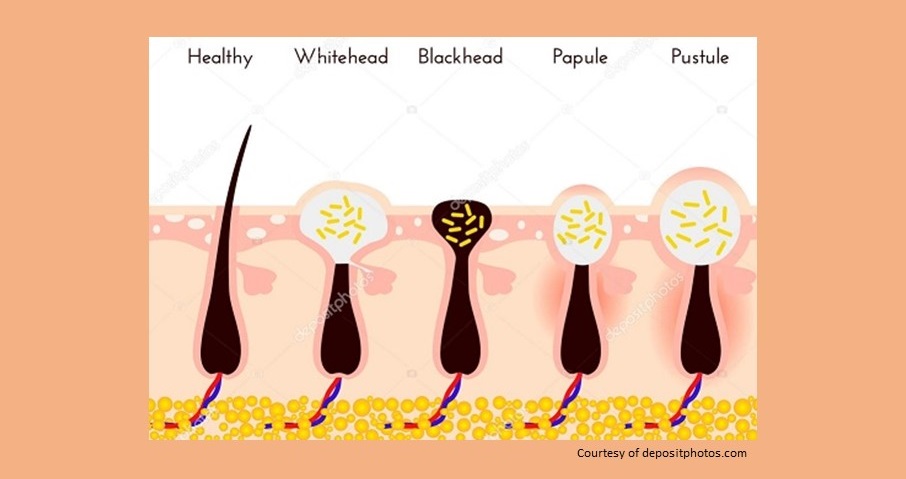
Pimples, whiteheads, and blackheads are the most common types of acne. They break out on the skin when a person’s hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. They do not pose any serious threat to health but can lead to prominent psychological and emotional issues.
Acne vulgaris, also commonly termed as acne, is a chronic and inflammatory disease of the glands that produce sebum. It's a prevalent skin disease in the African continent majorly affecting more females than males.1.
A special type of acne affecting the nape of the neck and common in black Africans is Acne Keloidalis Nuchae (AKN). It is an unusual form of hair follicle inflammation (folliculitis) that results in scarring hair loss around the nape of neck. AKN is 20 times more common in men than in women. It may persist for years and can be disfiguring.
.jpg)
Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
Causes of acne
The most commonly affected areas for acne are – face, chest, forehead, upper back, and shoulders. These areas have most of the sebaceous (oil) glands in our body, that is directly connected to hair follicles.
These oily glands produce a liquid called 'sebum' that carries the dead skin cells through follicles under the surface. When a small hair grows through the follicle and they are blocked by oil, the acne pops out.
Other factors that possibly cause acne:
• Rise in the hormone called androgen, which increases the oil glands under the skin. This in turn, producing excessive sebum and leads to flaring-up of acne.
• Medications that contain lithium
• Greasy cosmetics
• Obesity
• High-sugar diet
• Emotional Stress
• Mensuration can also trigger acne
Symptoms of acne
Acne is of two types – Inflammatory and Non-inflammatory.
Inflammatory acne is painful and leads to bumps of different types, whereas non-inflammatory acne isn't painful and doesn’t appear as bumps.
Inflammatory acne
They may cause more severe complications such as scarring and pitting. The different forms of inflammatory acne are:
Papules (Black or brown in color (in the African) and appear under the skin surface)
Pustules (Pimples)
Nodules (Painful, inflamed lumps deep within the skin)
Cysts (White lumps filled with pus)
Non-Inflammatory Acne
These don't swell and can be seen in any of the following forms:
Blackheads (Small, black, dark-colored spots appear mostly on the tip/side of the nose)
Whiteheads (Small, whitish colored spots appear on the tip and both sides of the nose)
.jpg)
Impact of acne
Chronic acne does have cosmetic effect on people. In addition, studies have also found that young people who are frequently prone to acne may suffer from such psychological issues1 such as:
Depression
Anxiety
Lack of self-love
Reduced self-esteem
Feel lonely and left out
Poor quality of a happy life
Treatment
Over-the-counter topical medications
Though there are various over-the-counter topical topical medications available for acne, it's best to consult a dermatologist for proper treatment. Listed below-are some over-the-counter medications that can be used for first line treatment of your acne:
Resorcinol - helpful in breaking down whiteheads and blackheads
Benzoyl peroxide - kills the acne-causing bacteria and slows down the glands' production of oil
Salicylic acid - slows the shedding of cells that line the follicles of the oil glands
Sulfur - has been used for centuries, slowly oxidizes the oily glands and has other anti-bacterial properties
Retin-A - unplugs the blocked pores
Azelaic acid - fortifies the line of follicles, stops oil eruption, and reduces bacterial growth. It is mainly found in wheat, rye, and barley.
Many cosmetics, mild shampoos, soaps, etc contain antiseptics which you can quickly use to stop those zits from appearing again and again.
Antibiotics
Oral antibiotics shoul be used sparingly in the treatment of acne. When indicated, it should be used only on a doctor's prescription at the beginning of treatment and for a short period in combination with non-antibiotic topical medications.
Home remedies
• Always remove your makeup before going to bed. Make sure you choose the best cosmetics that suit your skin
• Gently wash your face twice a day and apply a good moisturizer (having benzoyl peroxide) on your skin
• Avoid sun exposure
• Bursting the acne isn't encouraged as it may worsen the situation
• Applying honey over the affected area of your skin can be an effective remedy in fighting with zits
• Coconut oil, jojoba oil, or tea tree oil, when used directly or added to creams and cosmetics can be useful too
The Bottom Line
Acne can put a dent in your overall appearance and personality. With multiple options available, it’s a good practice to consult your family doctor or a dermatologist to understand what treatment will suit your skin.
If you still have some questions about acne, click here to ask our experts for answers.
Related article
Common hair and skin problems and how to treat them
References
Acne in South African black adults: A retrospective study in the private sector
Published: December 7, 2019
© 2019. Datelinehealth Africa Inc. All rights reserved.
DATELINEHEALTH AFRICA INC., is a digital publisher for informational and educational purposes and does not offer personal medical care and advice. If you have a medical problem needing routine or emergency attention, call your doctor or local emergency services immediately, or visit the nearest emergency room or the nearest hospital. You should consult your professional healthcare provider before starting any nutrition, diet, exercise, fitness, medical or wellness program mentioned or referenced in the DatelinehealthAfrica website. Click here for more disclaimer notice.