By Adeola Alabi. DLHA Volunteer and Freelance Health Writer. With medical review and editorial support from the DLHA Team.

Breast Health
A young African woman once asked me why she should be concerned about breast health despite no history of breast cancer in her family. I smiled and explained in detail.
Breast health is of utmost importance and requires regular practices to maintain healthy breasts.
These practices include breast self-exams, clinical breast exams by healthcare professionals, mammograms, and healthy lifestyle habits like regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol intake, and avoiding smoking.
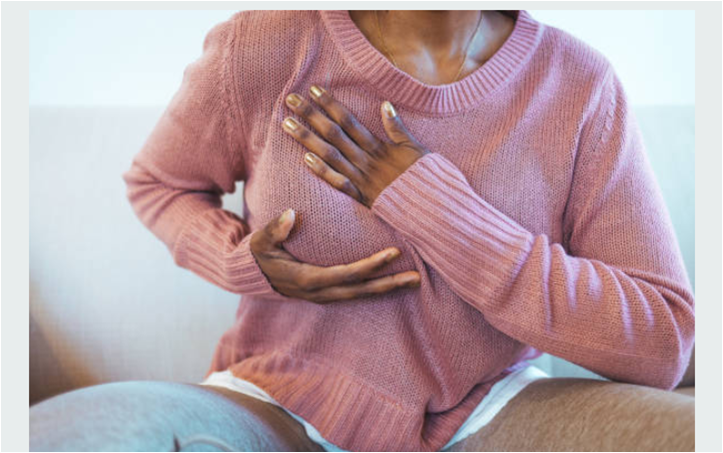
Black woman performing breast self examination
It's important to always keep an eye out for any changes in your breasts, including lumps, pain, or changes in size or shape. If you have any concerns, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare provider immediately. Regular breast health practices are essential for early detection of breast cancer and other breast-related issues.
The journey of breast development is a remarkable and complex process that happens in every woman's life during puberty.
It is a process of growth and maturation, driven by hormones like estrogen and progesterone. Starting with the formation of breast buds, it progresses through several stages, eventually leading to the development of mature breast tissue.
Along the way, the breasts may experience various changes that are a natural part of the process. While it is important to keep an eye out for any abnormal changes, understanding the journey of breast development can help every woman appreciate the beauty and uniqueness of her body.
Breast anatomy is complex, involving multiple structures that determine size, shape, and function.
Breast Structure
Breast size and shape can vary significantly among individuals and can be influenced by genetics, hormones, age, and lifestyle factors. Some common descriptors include:
Breast size is influenced by glandular and adipose tissue, genetics, hormones, pregnancy, and weight changes.
It is important to note that the size and shape of breasts can change over time due to various factors such as hormonal fluctuations during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, breastfeeding, menopause, weight changes, and ageing.
Regular breast self-examinations and clinical breast exams are important to monitor any changes in the breast and detect any abnormalities early.
Breast self-examination (BSE) is a simple yet important technique that you can perform regularly to detect any changes or abnormalities in your breast tissue.

Regular self breast examination is the foundation of breast health
It is a proactive approach to breast health that enables you to become familiar with the normal look and feel of your breasts, making it easier to detect any deviations that may signal a potential issue, such as breast cancer.

How to perform a breast self examination
If you notice any changes, such as a new lump, thickening, dimpling, or discharge, consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Rest assured that not all changes are indicative of breast cancer, but it's important to have any abnormalities assessed promptly.
Performing regular breast self-examinations can help you become more familiar with your breast and detect any changes early.
However, it's essential to remember that BSE should complement, not replace, regular clinical breast exams by healthcare professionals and mammograms as recommended by your healthcare provider based on your age, family history, and other risk factors.
Watch the video below to learn more about Breast Self Examination
Video: How to perform a breast self examination. Click on the image to view.
A mammogram is an X-ray picture used to detect breast tissue abnormalities, including early signs of cancer, before they cause noticeable symptoms. They play a crucial role in breast health.
Mammograms are an important tool in the management of breast health. They serve various purposes, such as detecting breast cancer at an early stage, screening women without any symptoms, evaluating symptoms or abnormalities, and monitoring breast health.
Early detection is crucial in increasing the chances of successful treatment and improving outcomes. Screening mammograms are typically recommended for women starting at age 40 or 50, depending on various factors such as family history, personal risk factors, and guidelines from healthcare professional organizations.
Mammograms can also be used for diagnostic purposes, providing more detailed images when there are symptoms or abnormalities detected during a clinical breast exam or self-examination. This helps healthcare providers evaluate any suspicious areas more closely.
Regular mammograms are recommended for women who have a history of breast cancer or other breast-related issues. They help monitor any changes in breast tissue over time and detect any recurrence of cancer or new abnormalities.
Three-dimensional (3D) mammography, also known as tomosynthesis, is an advanced imaging technique that provides clearer and more detailed images of breast tissue, especially in dense breasts. It helps reduce false-positive results and improves the accuracy of detecting breast cancer.
Mammograms raise awareness about the importance of breast health and early detection of breast cancer. They encourage women to prioritize regular breast screenings and take proactive steps to maintain their breast health.
Breast diseases include both benign and malignant conditions that affect the breast tissue.
Some common breast diseases include:
Early detection and regular breast screenings are crucial for the successful treatment of all of the above-mentioned diseases.
It’s important to consult your healthcare provider for any breast health concerns when you notice any changes or abnormalities in your breasts, regardless of your age or risk factors. Here are some specific situations when you should seek medical attention:
New Breast Lump or Mass: If you find a new lump or mass in your breast or armpit (axilla), it's crucial to have it checked by a healthcare professional. Although many breast lumps are benign, it's important to rule out the possibility of breast cancer through clinical examination and imaging tests.
Changes in Breast Size or Shape: Major changes in breast size, shape, contour, or symmetry should be evaluated by a doctor. This includes dimpling, puckering, or indentation of the breast skin, as well as changes in the appearance of the nipple or areola.
Breast Pain or Discomfort: Persistent or severe breast pain, tenderness, or discomfort not related to menstruation or does not resolve with the menstrual cycle should be evaluated by a healthcare provider. While breast pain is often benign, it can sometimes indicate a serious underlying issue that requires medical attention.
Skin Changes: Any unusual changes in the skin of the breast, such as redness, warmth, swelling, rash, or thickening, should be examined by a doctor. These changes could be signs of infection, inflammation, or, in some cases, breast cancer.
Nipple Changes: Changes in the appearance or texture of the nipple, such as inversion, flattening, scaling, crusting, or discharge (especially if bloody or spontaneous), should be investigated by a healthcare professional.
Family History of Breast Cancer: If you have a family history of breast cancer or other risk factors for the disease, you may benefit from discussing your concerns with a doctor and considering appropriate screening measures, such as genetic testing or earlier mammography.
Previous Breast Health Issues: If you have a history of breast disease, such as fibrocystic changes, fibroadenomas, or previous breast cancer, it's important to follow up with your healthcare provider for regular monitoring and surveillance.
In conclusion, breast health encompasses a comprehensive approach to maintaining the well-being of the breasts, including regular self-examinations, clinical evaluations, and screenings such as mammograms.
Overall, prioritizing breast health through awareness, screenings, and healthy lifestyle choices contributes to the well-being of individuals and communities. By fostering a culture of proactive breast health management and lactation support, you will be empowered to take control of your health and promote better outcomes for breast-related conditions.
USCF Health. Basic facts about breast health. [Internet, n.d.] accessed March 22, 2023. Available from here.
Breast density: What African women need to know
Breast cancer in Africa: What you need to know
Published: April 10, 2024
© 2024. Datelinehealth Africa Inc. All rights reserved.
Permission is given to copy, use and share content for non-commercial purposes without alteration or modification and subject to attribution as to source.
DATELINEHEALTH AFRICA INC., is a digital publisher for informational and educational purposes and does not offer personal medical care and advice. If you have a medical problem needing routine or emergency attention, call your doctor or local emergency services immediately, or visit the nearest emergency room or the nearest hospital. You should consult your professional healthcare provider before starting any nutrition, diet, exercise, fitness, medical or wellness program mentioned or referenced in the DatelinehealthAfrica website. Click here for more disclaimer notice.