6 Ways Cigarette Smoking Causes Erectile Dysfunction with Tips on Solutions
Salman Afzal, MBBS, UKMLA, MS, DLHA Volunteer and Freelance Health Writer. Medically reviewed by C. Akpa. B. Pharm.

Composite image of a stubbed cigarette and a bedroom scene showing an African man in the foreground looking sad with a blurry image of a woman in the background.
Cigarette smoking in Africa is a growing public health concern with significant implications for both health outcomes and economic costs.
Cigarette smoking is one of the leading causes of erectile dysfunction. In today's world where erectile dysfunction (ED) is still a taboo, there is a need to raise the public’s awareness about the contribution of cigarette smoking to ED with the hope of improving men’s sexual performance and reproductive health generally.
In this article you will learn about how cigarette smoking leads to erectile dysfunction, ways to quit smoking and regain your sexual health after smoking cessation.
Smoking in Africa remains relatively low compared to other regions, though it varies significantly across countries and demographics:
Overall prevalence among adults is estimated at 8.4–10.3%, with projections showing a slight decline—from 10.3% in 2020 to around 9% by 2025. [1]
Daily smoking in Sub-Saharan Africa averaged about 3.5% for all adults (18+) between 2018 and 2023; lifetime prevalence was ~12.7%, and past year prevalence was ~12.1%, while youth (10–17 years) recorded a prevalence of ~ 4.5% in ever-smoked, ~ 4.1% past year, and ~ 4.7% daily. [1]
The major harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke include:
Nicotine: This is a highly addictive substance found in tobacco addiction. It increases heart rate and blood pressure.
Tar: Is a sticky brown substance containing many cancer causing chemicals. It is formed from burning tobacco. It causes lung damage and cancer.
Carbon monoxide: This is a colorless and odourless gas that is generated from the combustion of cigarettes. It reduces oxygen delivery and increases heart disease risk.
Benzene: This is a known carcinogen (cancer causing product) and also a petroleum by-product. It causes bone marrow damage and leukemia.
Polonium-210: Is a radioactive element found in tobacco leaves. It emits radiation and increases cancer risk.
Arsenic: Is a toxic metal that causes skin, lung, and bladder cancer. It is used in rat poison.
Formaldehyde: This is a toxic cancer causing chemical that is irritant to the eyes, nose and lungs. It is also used in preserving dead bodies.
Ammonia: Is found in many common household cleaning agents. It is added to tobacco to increase its impact.
Acetone: Is a highly inflammable and evaporative substance that causes eye, nose, and throat irritation. It is also found in nail polish remover.
Hydrogen cyanide: This is a toxic gas that can damage the lungs. It interferes with oxygen use in cells and is used in gas chambers.
Nitrosamines: They are potent carcinogens (cancer causing agents) that are formed during tobacco curing and processing.
Tobacco use is linked to various diseases and is a major risk factor for numerous chronic non-communicable diseases such as cancer, heart disease, lung diseases, stroke, and diabetes.
In 2019, tobacco consumption led to around 200 million Disability Adjusted Life Years lost and caused approximately 7.65 million deaths worldwide.
In South Africa, over 32,000 deaths annually are attributed to tobacco-related illnesses, including cardiovascular diseases, which account for 22% of these deaths. Tobacco use also contributes to 13% of non-communicable disease deaths in the country. [2]
In Zambia, tobacco consumption leads to approximately 7,100 deaths annually, with significant mortality from cardiovascular diseases. [2]
In Ethiopia, tobacco use is responsible for over 9,884 deaths annually, contributing to 5% of all non-communicable disease deaths, with 29% of these deaths attributed to cardiovascular diseases. [2]
While there are numerous side effects of cigarette smoking, in this article we will particularly focus on the effects of smoking on erection.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the persistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. It is one of the most common sexual health problems in men.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is very common in Africa, especially with the rise of chronic diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and obesity, which are major risk factors.
Although ED is often underreported in African countries due to cultural stigma, lack of awareness, and limited data, its estimated rate of occurrence in Sub-Saharan Africa and different African countries are shown in Table 1 below:
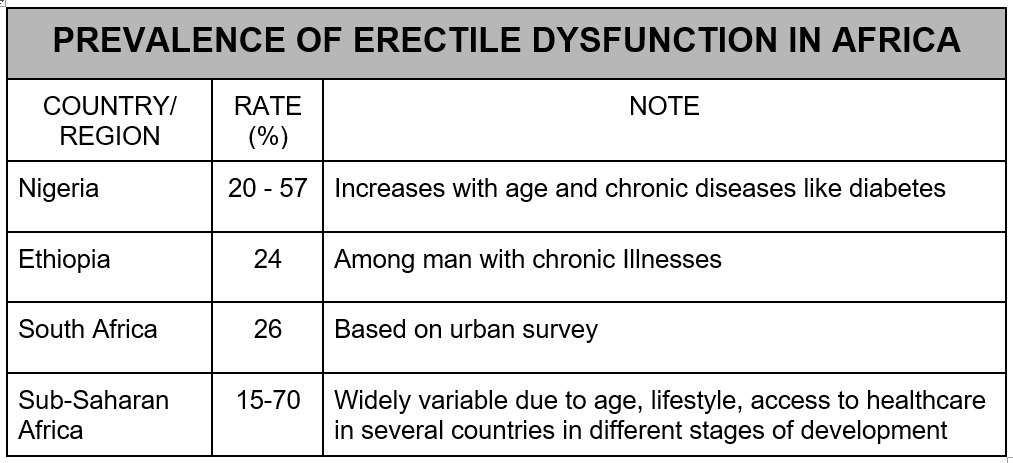
Table 1: showing prevalence of erectile dysfunction in some African countries and in the sub-Saharan Africa region. [3]
ED can be caused by:
In order to fully appreciate how smoking causes erectile dysfunction, you need to know how normal erection occurs.
Anything that interferes or disrupts the above processes in any way, leads to erectile dysfunction.
As explained in the normal process of erection, when vessels supplying blood to the penis dilate, blood rushes into penile muscles to cause erection. Any cause of narrowing of these vessels contributes to erectile dysfunction.
Smoking damages the lining of blood vessels (endothelium) and promotes atherosclerosis (narrowing and hardening of arteries).
Also with long term smoking, the multiple harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke, causes hardening of smooth muscles in walls of vessels of the body generally, including those to the heart, brain, kidneys and penis.
Nicotine present in cigarettes specifically causes vasoconstriction (reduction in the size of blood vessels). It also damages muscles in penile tissues to cause these muscles to contract resulting in reduction in penile size.
In effect, cigarette smoking reduces blood flow to the muscles of the penis, making it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection.
Nitric oxide (NO) is a molecule and gas that is released naturally in the body including from the lining of blood vessels.
In the penis, NO is essential for relaxing the smooth muscles of its blood vessels thereby allowing blood to flow to cause erection.
Chemicals in cigarette smoke inhibit nitric oxide production, to interfere with the process of erection.
Many of the chemicals in cigarette smoke including carbon monoxide, tar, formaldehyde, etc., contribute to increased oxidative stress and inflammatory responses. These contribute to vascular and nerve damage—both key in the development of erectile dysfunction.
Chronic smoking may slightly lower testosterone levels, a hormone critical for libido and erectile function.
Nicotine also stimulates adrenaline release, which causes blood vessels to constrict (the opposite of what's needed for an erection).
Smoking can impair nerve function, including the nerves responsible for erection. Harmful chemicals in cigarettes affect the myelin sheath of neurons. This myelin sheath is responsible for maintaining the health of nerve cells. This is especially problematic in men with other conditions like diabetes.
Smoking is linked with increased anxiety and depression, both of which can worsen or cause ED.
Anxiety and depression causes activation of the sympathetic nervous system. Sympathetic surge increases adrenaline release to cause penile vessels to remain contracted, leading potentially to ED.
Relationship problems are variously associated with stress, anxiety, depression, and reduced libido.
Evidence from Studies
A meta-analysis found that smokers are twice as likely to have ED as non-smokers. BJU International studies 2015 showed 21.5% smokers had ED, while only 12.5% non-smokers had ED.(4)
Quitting smoking improves erectile function in many men, especially those under 50.
As cigarette smoking significantly affects penile erection, it stands to reason that quitting smoking would be an important requirement in managing erectile dysfunction in smokers.
So here are some practical steps you can take to quit smoking.
Quitting smoking is tough, but completely possible with the right approach and support. When you quit smoking and couple it with healthy lifestyle choices that includes a balanced diet [5], exercise, quality sleep and minimal use of alcohol, you will be on your road to a natural recovery from smoking related erectile dysfunction and achieving satisfactory sexual health. .
Here are effective ways to quit smoking, backed by evidence and real-world success:
These help reduce withdrawal symptoms and include:
They work best when combined with behavioral support.
Talk to your doctor before starting any medications.
Apps like QuitNow, Smoke Free, and MyQuit Coach help track progress and keep you motivated.
Many offer daily tips, community support, and goal tracking.
One-on-one or group counseling improves quit rates significantly.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) can help rewire the way you think about smoking.
Some succeed by stopping abruptly without aid. Success depends on willpower, support, and avoiding triggers.
Mindfulness meditation can reduce cravings. Acupuncture and hypnotherapy work for some, though evidence is mixed.
Conclusion
Cigarette smoking affects men's health in various ways. Chemicals present in cigarettes and cigarete smoke like nicotine, tar, carbon monoxide and aromatic substances (benzene and acetone) cause Several studies have indicated causal association between erectile dysfunction and cigarette smoking. There are numerous ways to quit smoking. Every method has its own importance and results. When you quit smoking and make healthy lifestyle choices, your erectile dysfunction can improve significantly..
1. Belete H, Mekonen T, Connor JP, Chan G, Hides L, Leung J. Tobacco smoking in Sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2025 May;44(4):1079-1091. doi: 10.1111/dar.14040. Available from here.
2. Zhao L, Palipudi KM, Ramanandraibe N, Asma S. Cigarette smoking and cigarette marketing exposure among students in selected African countries: Findings from the Global Youth Tobacco Survey, Preventive Medicine, 2016; Volume 91, Supplement, Pages S35-S39. doi: org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2015.12.015. Available from here.
3. Zedan H, Hareadei AA, Abd-Elsayed AA, Abdel-Maguid EM. Cigarette smoking, hypertension and diabetes mellitus as risk factors for erectile dysfunction in upper Egypt. East Mediterr Health J. 2010 Mar;16(3):281-5. Available from here.
4. McVary KT, Carrier S, Wessells H. Smoking and erectile dysfunction: evidence based analysis. The Journal of urology. 2001 Nov 1;166(5):1624-32. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)65641-8. Available from here.
5 Esposito K, Giugliano F, Maiorino MI, Giugliano D. Dietary factors, Mediterranean diet and erectile dysfunction. The Journal of Sexual Medicine. 2010 Jul;7(7):2338-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2010.01842.x. Available from here.
Related:
Published: June 2025
© 2025. Datelinehealth Africa Inc. All rights reserved.
Permission is given to copy, use and share content for non-commercial purposes without alteration or modification and subject to attribution as to source.
DATELINEHEALTH AFRICA INC., is a digital publisher for informational and educational purposes and does not offer personal medical care and advice. If you have a medical problem needing routine or emergency attention, call your doctor or local emergency services immediately, or visit the nearest emergency room or the nearest hospital. You should consult your professional healthcare provider before starting any nutrition, diet, exercise, fitness, medical or wellness program mentioned or referenced in the DatelinehealthAfrica website. Click here for more disclaimer notice.